Introduction
NetBird is a unified connectivity platform combining a WireGuard configuration-free peer-to-peer private network and a centralized access control system making it easy to create secure private networks for your organization or home.
This tutorial provides a complete walkthrough for integrating NetBird with a Hetzner server to establish a secure, unified private network. We will detail every step, including provisioning the necessary Private Network and cloud servers, configuring a generic NAT gateway, and connecting your devices (peers) using NetBird. Upon completion, you will have seamless, secure access to all resources within your Private Network from any connected device.
Prerequisites
- A public domain address
Example terminology
| Name | Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Domain | example.com | Your public domain. |
| Network IP range | 192.168.0.0/16 | Your network range, defined during network creation. |
| NAT server (Public IPv4) | 203.0.113.1 | The internet-facing IPv4 address assigned to your NAT server after creation. |
| NAT server (Network IPv4) | 192.168.0.2 | The network IPv4 assigned to your NAT server. |
| Client server (Network IPv4) | 192.168.0.3 | The network IPv4 assigned to your private server, make sure to select a reserved address. |
Step 1 - Creating the necessary infrastructure
We will now create the necessary cloud infrastructure to host NetBird and give it access to a private server.
Open the Hetzner Console and select your project.
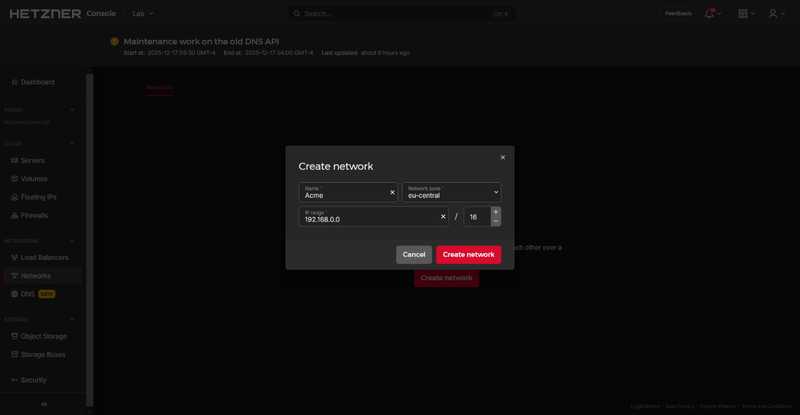
You have the option to create the Network first or to create it during the server creation process, we'll opt for creating our network beforehand.
-
Creating a NAT server
Select
Cloud->Servers->Add Server.In the section "Networking":
- Tick "Public IPv4"
- Attach this server to the previously created network.
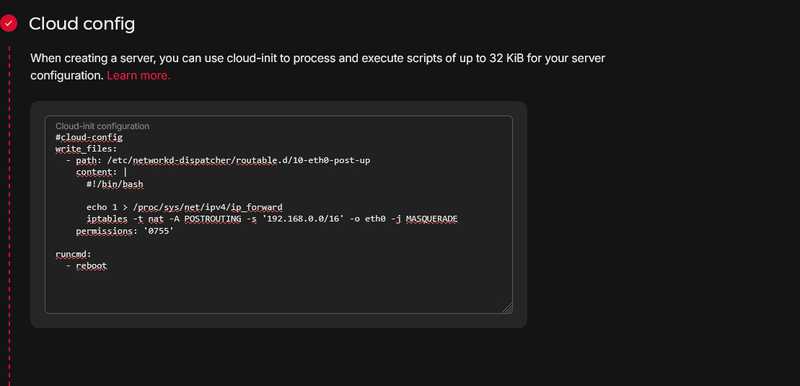
For easier setup, we'll be using the prewritten Cloud-init files found on the NAT gateway for private Cloud Networks setup guide. For the network, use
192.168.0.0/16instead of10.0.0.0/16.
-
Creating a client server
Once again select
Cloud->Servers->Add ServerIn the section "Networking":
- Untick public IPs
- Attach this server to the previously created network.
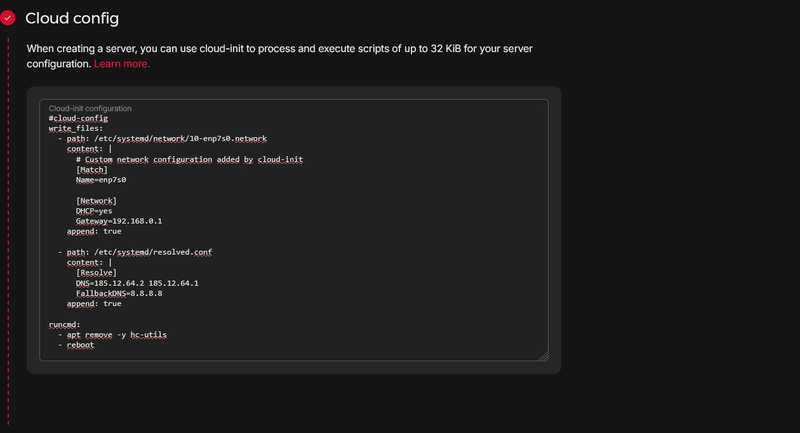
Set up the Cloud-init for client servers found in the guide. For the gateway, use
192.168.0.1instead of10.0.0.1.
-
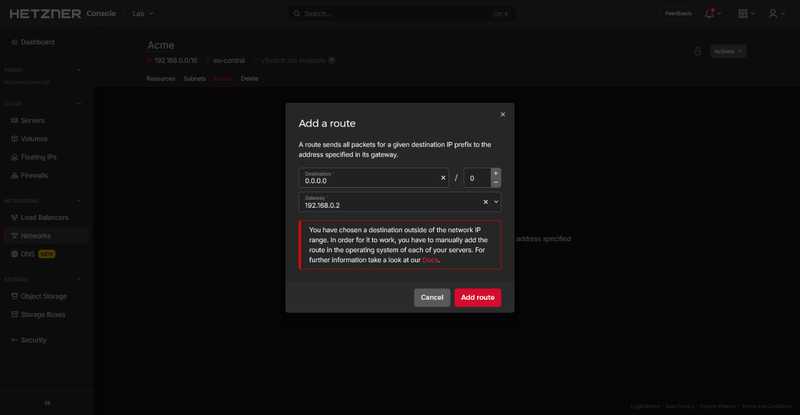
Creating a network route
Select
Networking->Networksand select the previously created network, then selectRoutes->Add route, then set the following values:Value Notes Destination 0.0.0.0/0 This signifies that the destination can be any possible IPv4 address, allowing our local network to access the internet. Gateway 192.168.0.2 This is our NAT server's network IPv4.
With this done, our NAT setup should be completed, let's connect to our private server and run some tests. We'll first test if we can ping Google's public DNS server 8.8.8.8, then we'll test pinging a domain itself. If our setup was successful, we should have no packet loss.
# Test internet connectivity
ping -c 3 8.8.8.8
# Test namespace resolution
ping -c 3 google.comThe
-c 3flag in thepingcommand is letting our server know that once 3 ping attempts are done it should stop executing
Step 2 - Configuring the DNS record
We will now configure our DNS record so that our domain points to our NAT server, allowing us to install and set up NetBird.
In your DNS manager, create the following A record:
Important: If using CloudFlare, make sure to disable the
Proxyingon your record as it is known to cause issues.
| Type | Name | Content | TTL |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | netbird | 203.0.113.1 | Automatic |
This DNS record is telling our domain registrar that our subdomain netbird.example.com should point to our NAT's public IPv4.
While you can use your main domain (
example.com) for setting up NetBird, it is recommended that you set up theArecord with a subdomain (sub.example.com) instead.
Step 3 - Installing and Setting up NetBird
We will now proceed to install NetBird on our NAT server, so that it can be used as a bridge to reach our private server in the network we created.
For our NetBird installation, we'll be following the Self-hosting quick start guide, which will give us a running instance of NetBird using Zitadel as our IDP (Identity Provider)
Before installing anything, let's make sure that our system is up to date.
Connect to the server with the public IPv4 and upgrade your system:
The NAT server used in this example is running Ubuntu 24.04, make sure to use the appropriate package manager for your server.
apt update && apt upgrade -yAfter that, we should install Docker as explained in the official docs:
Once Docker is installed on our server, we need to make sure we have the curl and jq packages installed:
apt install jq curlOnce all the requirements are met, we can download and execute the NetBird installation script:
export NETBIRD_DOMAIN=netbird.example.com; curl -fsSL https://github.com/netbirdio/netbird/releases/latest/download/getting-started-with-zitadel.sh | bashOnce the installation is complete, you can access your NetBird instance via your NETBIRD_DOMAIN using the credentials shown in your terminal.
Once we complete the initial user setup via Zitadel, we'll be met with a NetBird welcome page. Simply select Skip to Dashboard.
Step 4 - Setting up a Zitadel account (Optional)
As previously stated, this instance of NetBird uses Zitadel as an identity provider, we'll now use Zitadel to create a new account to access NetBird.
Go to https://netbird.example.com/ui/console to access the Zitadel console.
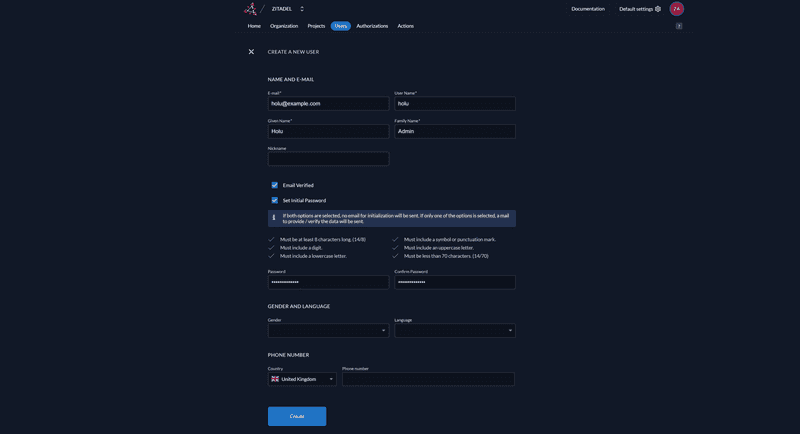
Once in the Zitadel console, select Users -> New and create a new Zitadel user.
It is important that you check both the
Email verifiedandSet Initial passwordcheckboxes, since this server currently has no SMTP configuration.
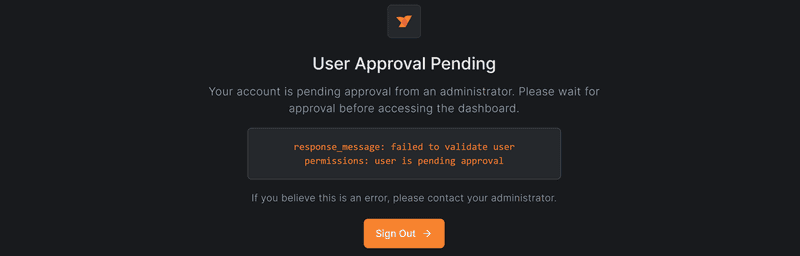
Once the user is created, if we attempt to log in at https://netbird.example.com with it we'll be met with a User Approval Pending screen. This is because we first have to approve the user in our NetBird dashboard. You have to try logging in and log back out, or else you cannot approve the user in the next step.
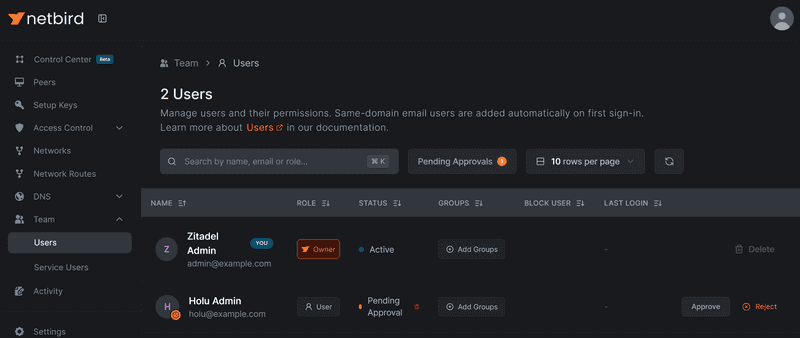
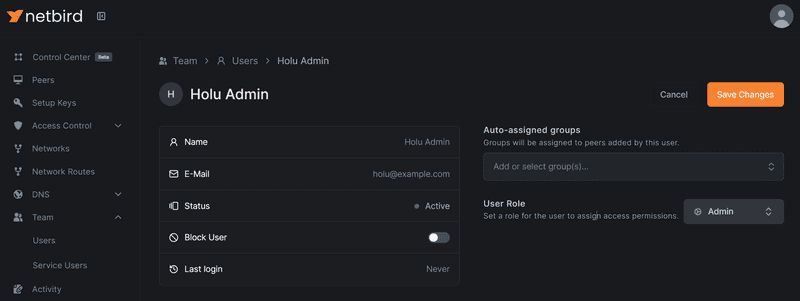
Once again, log in at https://netbird.example.com with the default admin account created. Select Team -> Users and select the Approve option on the new Zitadel user. While at it, let's assign the Admin role to it.
With this done, the newly created account can be used to access NetBird.
Step 5 - Connecting our server to NetBird
NetBird calls every device connected to the network a Peer, each Peer can be assigned to a group for access control and connection rules.
We'll start by connecting our private server to our NetBird network, we'll do this with a Setup Key that will auto assign any peer created with said key to a group.
While optional, it is recommended that you use Setup Keys when adding new devices to your network
Select Setup Keys -> Create Setup Key:
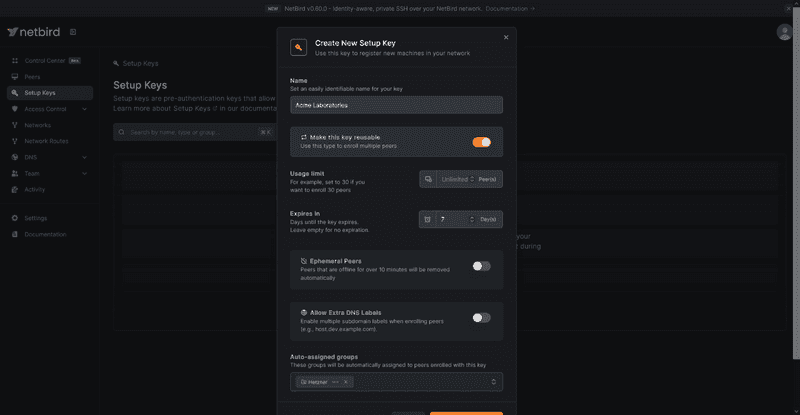
For this example, we'll create a Acme Laboratories setup key, make it reusable for 7 days, and auto assign every machine connected with this setup key to a Hetzner group.
Once the creation is complete and you select "Install NetBird", NetBird will prompt you with the necessary commands to connect a new peer using the Setup Key.
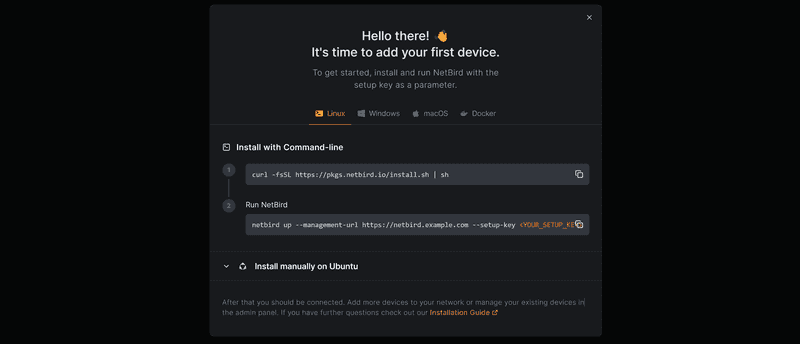
Connect into your private server and execute the command as prompted by NetBird, first we'll install NetBird:
curl -fsSL https://pkgs.netbird.io/install.sh | shThen we'll connect to our NetBird instance using our setup key:
sudo netbird up --management-url https://netbird.example.com --setup-key <YOUR_SETUP_KEY> If done correctly, our terminal will return an output of Connected, signalling us that the connection has been successful, we can see our private server now connected to NetBird in the Peers section of the dashboard.

Conclusion
You have successfully built your own cloud network, configured a NAT gateway to allow internet access for your private resources, and deployed NetBird to safely access those resources from anywhere.
NetBird provides a unified FOSS platform for reliable and secure connectivity, giving you full control over who gains access to your cloud and on-premises resources, and how.
For further steps, browse how to connect other devices to your NetBird network, as well as how to provide SSH access to peers in your network. Additionally, to learn how to manage your access control via Zitadel read their official documentation.