Introduction
If your WordPress site fails during plugin installs, media uploads, imports, or bulk updates, you are often hitting resource ceilings rather than a WordPress bug.
This tutorial shows how to increase the most common limits on an Ubuntu server running Apache:
- WordPress memory constants (
WP_MEMORY_LIMIT,WP_MAX_MEMORY_LIMIT) - PHP
memory_limit - PHP
upload_max_filesize - PHP
post_max_size
For background on how WordPress relates to these PHP directives, see the WordPress Developer Handbook page "PHP Optimization".
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu with SSH access (for example, a Hetzner cloud server)
- A working WordPress installation
- Admin access to the server (root or a sudo-capable user)
- A text editor available on the server (
nanoorvim)
Example terminology
This tutorial uses placeholders like:
- Username:
holu - IP address:
YOUR_SERVER_IP - Domain:
YOUR_DOMAIN - WordPress root:
/var/www/html
Replace them with your own values.
Step 1 - Connect via SSH and locate your WordPress root
SSH to the server:
ssh holu@YOUR_SERVER_IPA common WordPress root on Apache installs is:
cd /var/www/html
ls -laYou should see wp-config.php and directories such as wp-content/, wp-admin/, and wp-includes/.
If you do not see wp-config.php, search for it:
sudo find /var/www -type f -name wp-config.php 2>/dev/nullThen cd into the directory that contains it.
holu@example:~$ cd /var/www/html
holu@example:/var/www/html$ ls -la
total 248
drwxr-xr-x 5 www-data www-data 4096 Dec 29 10:01 .
drwxr-xr-x 3 www-data www-data 4096 Dec 28 16:25 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 704 Dec 29 10:00 .htaccess
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 405 Feb 6 2020 index.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 19903 Dec 28 16:38 license.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 7425 Dec 28 16:38 readme.html
drwxr-xr-x 9 www-data www-data 4096 Nov 21 2024 wp-admin
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 351 Feb 6 2020 wp-blog-header.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 3323 Jun 14 2023 wp-comments-post.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 3652 Dec 29 09:58 wp-config.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 3339 Dec 28 16:38 wp-config-sample.php
drwxr-xr-x 7 www-data www-data 4096 Dec 28 16:38 wp-content
drwxr-xr-x 31 www-data www-data 12288 Dec 28 16:38 wp-includes
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 2493 Dec 28 16:38 wp-links-opml.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 3937 Mar 11 2024 wp-load.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 51437 Dec 28 16:38 wp-login.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 8727 Dec 28 16:38 wp-mail.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 31055 Dec 28 16:38 wp-settings.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 34516 Dec 28 16:38 wp-signup.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 5214 Dec 28 16:38 wp-trackback.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 3205 Dec 28 16:38 xmlrpc.php
holu@example:/var/www/html$Step 2 - Back up configuration files
From the WordPress root directory, back up wp-config.php:
sudo cp -a wp-config.php wp-config.php.bak.$(date +%F)Back up .htaccess if it exists:
test -f .htaccess && sudo cp -a .htaccess .htaccess.bak.$(date +%F)Step 3 - Increase WordPress memory limits in wp-config.php
WordPress has its own memory configuration constants that you can set in wp-config.php. The WordPress Developer Handbook documents these constants and explains how they interact with PHP's memory_limit.
Edit wp-config.php:
sudo nano wp-config.php
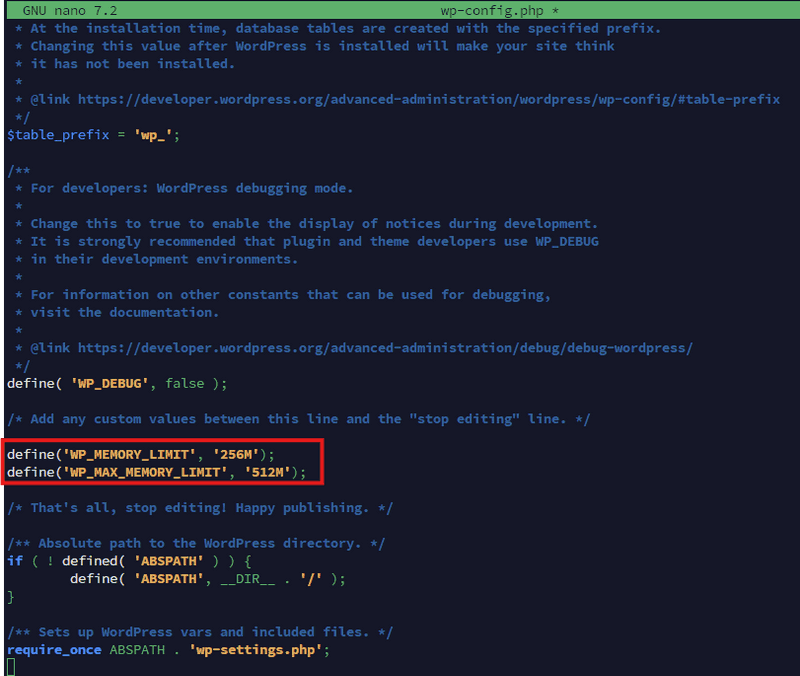
# or: sudo vim wp-config.phpAdd the following lines above the line that says "That's all, stop editing":
define('WP_MEMORY_LIMIT', '256M');
define('WP_MAX_MEMORY_LIMIT', '512M');Save and exit.
Notes:
WP_MEMORY_LIMITapplies to frontend rendering.WP_MAX_MEMORY_LIMITapplies to admin and logged-in contexts, and is commonly relevant for media operations.- WordPress cannot exceed the PHP memory limit if PHP is capped lower than these values.
Step 4 - Check how PHP is connected to Apache
Whether you can set PHP directives in .htaccess depends on how PHP runs behind Apache.
Run:
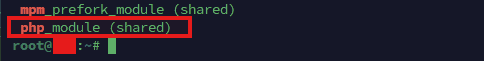
apache2ctl -M | grep -E 'php|proxy_fcgi|mpm'Interpretation:
- If you see
php_module, Apache is using mod_php and.htaccessdirectives likephp_valuetypically work. - If you see
proxy_fcgi_module, the site is often using PHP-FPM, andphp_valuein.htaccessmay cause a 500 error.
Step 5 - Increase PHP limits (recommended approach for mod_php)
The WordPress Cloud App image from Hetzner installs Apache2 and WordPress along with PHP extensions.
Option A - Use .htaccess (recommended when apache2ctl shows php_module)
If Step 4 shows php_module, add PHP limits to the WordPress .htaccess file.
Edit .htaccess in the WordPress root:
sudo nano .htaccess
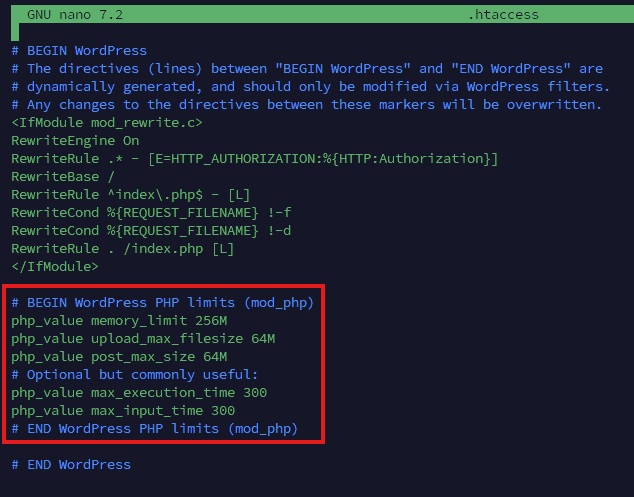
# or: sudo vim .htaccessAdd this block near the top (or near the existing WordPress section):
# BEGIN WordPress PHP limits (mod_php)
php_value memory_limit 256M
php_value upload_max_filesize 64M
php_value post_max_size 64M
php_value max_execution_time 300
php_value max_input_time 300
# END WordPress PHP limits (mod_php)The WordPress Developer Handbook notes that upload sizes are controlled by PHP upload_max_filesize and post_max_size, and that post_max_size must be greater than or equal to upload_max_filesize.
Option B - If .htaccess is not supported (PHP-FPM), use .user.ini
If adding php_value triggers a 500 error, you are likely not running mod_php. In that case, use .user.ini instead.
Create or edit .user.ini in your WordPress root:
sudo nano .user.iniAdd:
memory_limit=256M
upload_max_filesize=64M
post_max_size=64M
max_execution_time=300
max_input_time=300Save and exit.
Step 6 - Restart services and verify the new limits
Restart Apache:
sudo systemctl restart apache2If you are using PHP-FPM, restart it too (replace VERSION):
sudo systemctl restart phpVERSION-fpmExamples:
sudo systemctl restart php8.2-fpm
sudo systemctl restart php8.3-fpmVerify in WordPress Site Health
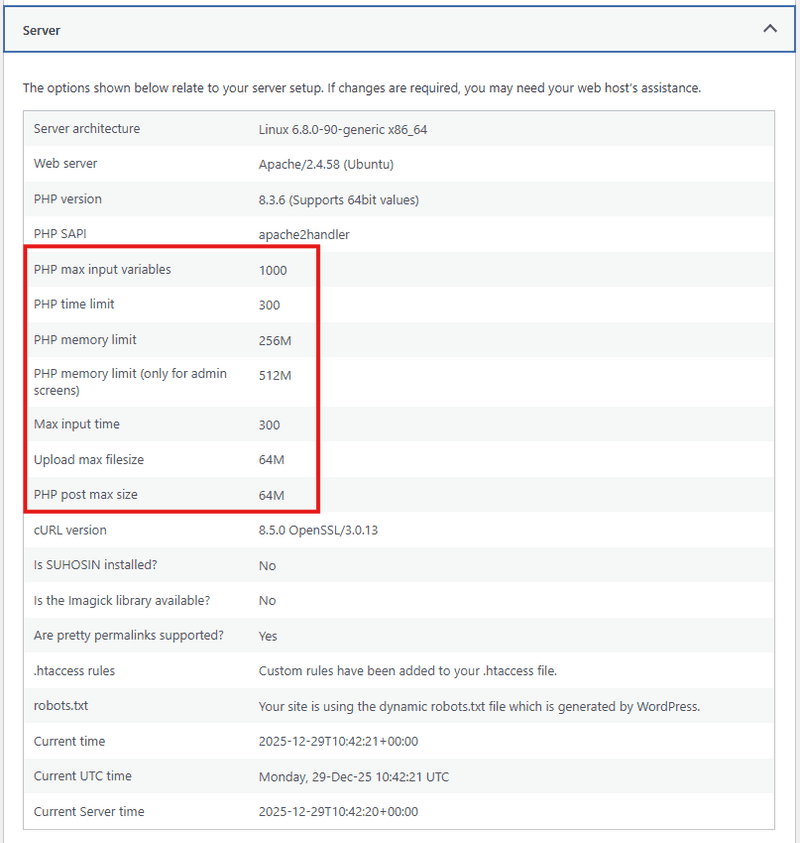
- In WordPress admin at
YOUR_DOMAIN/wp-admin, go to Tools -> Site Health - Open the Info tab
- Check values such as memory limits and maximum upload size
https://YOUR_DOMAIN/wp-admin/site-health.phpVerify with phpinfo (temporary)
Create a temporary file:
echo "<?php phpinfo();" | sudo tee /var/www/html/phpinfo.php >/dev/nullOpen http://YOUR_DOMAIN/phpinfo.php and verify:
memory_limitupload_max_filesizepost_max_size
Then remove the file immediately:
sudo rm -f /var/www/html/phpinfo.phpStep 7 - Troubleshooting and rollback
500 Internal Server Error after editing .htaccess
Likely causes:
- The server uses PHP-FPM (FastCGI), so
php_valuedirectives are not allowed in.htaccess. - A directive was mistyped.
.htaccessoverrides are disabled.
Fix:
-
Restore your
.htaccessbackup (if you made one in Step 2):sudo cp -a .htaccess.bak.$(date +%F) .htaccessIf you do not have a backup, remove only the block you added.
-
Restart Apache:
sudo systemctl restart apache2 -
Use Step 5 Option B (
.user.ini) or set the values inphp.ini/ PHP-FPM pool configuration.
Upload size does not increase
Double-check these points:
post_max_sizeis greater than or equal toupload_max_filesize.- A reverse proxy, WAF, or CDN is not enforcing its own request size limits.
- WordPress is not constrained by an application-level restriction in a plugin.
Conclusion
You have now:
- Increased WordPress memory limits via
wp-config.php - Increased PHP memory and upload limits using the approach that matches your PHP runtime
- Verified the result and captured rollback steps