Introduction
This tutorial helps you through setting up an Xray proxy server using the Shadowsocks protocol, deployed on Rocky Linux via Docker.
What is Xray?
Xray is a core engine that powers advanced proxy tools. It is an alternative to the V2Ray core and supports multiple proxy protocols (such as Shadowsocks, VLESS, etc.). It provides features such as load balancing, routing, obfuscation, and traffic encryption.
At the moment, it has over 30k stars on GitHub.
What is Shadowsocks?
Shadowsocks is an open-source proxy tool designed to help people bypass internet censorship and protect their online privacy.
Shadowsocks works by using a technique called SOCKS5 proxying, which allows internet traffic to be tunneled securely through a server.
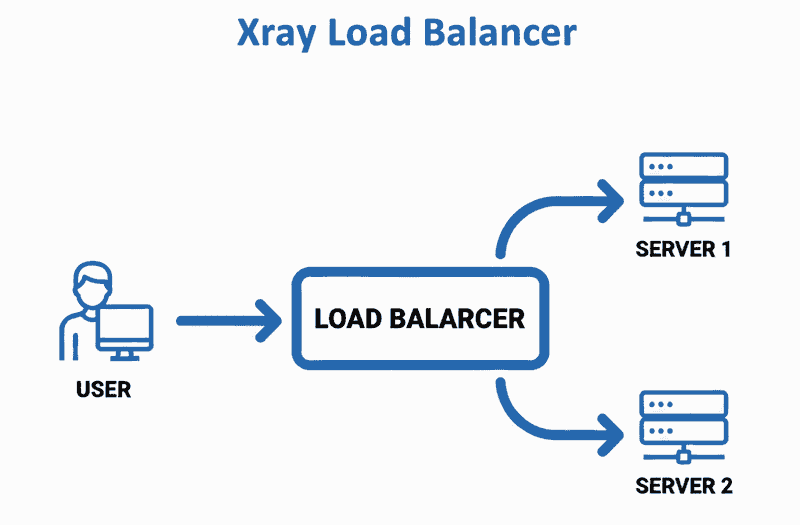
I will configure a load balancer setup with 3 servers.
One acting as the load balancer (LB) and two as backend servers.
Traffic from clients will hit the LB server, which routes it to the backends using Xray's built-in load balancer in the routing section.
Prerequisites
- Three Hetzner Cloud servers running Rocky Linux 10 (or later).
LBServer: Public IP for client access.- Backend Servers: Internal or public IPs accessible from
LB.
rootorsudoaccess on all servers.- Shadowsocks client on your local machine.
- Firewalls allow the necessary ports for Shadowsocks, e.g.:
4700for theLBserver4800for the backend servers
Example terminology
Replace all example IPs with your actual Hetzner server IPs.
LBServer:203.0.113.1- Backend Servers:
10.0.0.2and10.0.0.3
Step 1 - Install Docker
I purchased three Rocky Linux 10 VPS instances on Hetzner Cloud.
You need to install Docker on all of your Rocky Linux instances. If you are using a different Linux distribution, follow the steps provided on the official Docker website.
# Update your instance
dnf -y update
# Install useful packages
dnf -y install \
epel-release \
bash-completion
# Reboot your Linux instance
reboot# Add Docker repo
dnf config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
# Install Docker
dnf -y install \
docker-ce \
docker-ce-cli \
containerd.io \
docker-compose-plugin
# Enable and start Docker service
systemctl --now enable dockerStep 2 - Setting Up the Servers
We will deploy Xray in Docker on each server.
Create a directory for the configs on each server:
mkdir -p /etc/xrayStep 3 - Server Configuration files
Xray uses JSON configs. All files use the Shadowsocks protocol with the method aes-128-gcm.
Create the following file on all servers:
/etc/xray/config.jsonThe content of config.json on the LB server is different to the content on the backend servers.
-
Load Balancer Server Config
This config has a Shadowsocks inbound for clients, two outbounds to backends, and a balancer in
routingto distribute traffic.Notes:
- The
LBusesround-robinstrategy to distribute traffic between the backend servers. - Restart containers after config changes:
docker restart xray_lb(orxray_backend).
Add the following content in
/etc/xray/config.jsonon theLBserver:Load Balancer config file
Replace
10.0.0.2and10.0.0.3with the actual IPs of Server 1 and Server 2.// vi /etc/xray/config.json { "log": { // https://xtls.github.io/en/config/log.html "loglevel": "none" // debug | info | warning | error | none }, "inbounds": [ { "tag": "shadow_in", "protocol": "shadowsocks", "listen": "0.0.0.0", "port": 4700, "settings": { // https://xtls.github.io/en/config/inbounds/shadowsocks.html "email": "c1", "password": "xkONm1pWtKo0YcLD7Sxcog==", // openssl rand -base64 16 "method": "aes-128-gcm", "network": "tcp" } } ], "outbounds": [ // Server 1 { "tag": "shadow_server_1", "protocol": "shadowsocks", "settings": { // https://xtls.github.io/en/config/outbounds/shadowsocks.html "servers": [ { "email": "server_1", "address": "10.0.0.2", // Server 1 IP "port": 4800, "password": "PMTXZ5mkJhC508za5dBqeQ==", "method": "aes-128-gcm", "uot": false } ] } }, // Server 2 { "tag": "shadow_server_2", "protocol": "shadowsocks", "settings": { "servers": [ { "email": "server_2", "address": "10.0.0.3", // Server 2 IP "port": 4800, "password": "PMTXZ5mkJhC508za5dBqeQ==", "method": "aes-128-gcm", "uot": false } ] } } ], "routing": { // https://xtls.github.io/en/config/routing.html "domainStrategy": "AsIs", // AsIs | IPIfNonMatch | IPOnDemand "balancers": [ { "tag": "main_balancer", "selector": ["shadow_server_"], // Will be matched shadow_server_1 and shadow_server_2 "strategy": { "type": "roundRobin", // random | roundRobin | leastPing | leastLoad "settings": {} } } ], "rules": [ { "inboundTag": "shadow_in", "balancerTag": "main_balancer" } ] } } - The
-
Backend Servers Config
A simple inbound from
LB, and an outbound to freedom (direct internet).Add the following content in
/etc/xray/config.jsonon the backend servers:Backend servers config file
Use this config on both backend servers. Set
"email": "server_1"for Server 1 and"email": "server_2"for Server 2.// vi /etc/xray/config.json { "log": { "loglevel": "none" }, "inbounds": [ { "tag": "shadow_in", "protocol": "shadowsocks", "listen": "0.0.0.0", "port": 4800, "settings": { "email": "server_1", // server_1 and server_2 "password": "PMTXZ5mkJhC508za5dBqeQ==", "method": "aes-128-gcm", "network": "tcp" } } ], "outbounds": [ { // https://xtls.github.io/en/config/outbounds/freedom.html "tag": "free", "protocol": "freedom", "settings": {} } ], "routing": { "domainStrategy": "AsIs", "rules": [ { "inboundTag": "shadow_in", "outboundTag": "free" } ] } }
Step 4 - Setting Up the Servers
Load Balancer Server Setup
On the LB server (e.g., IP: 203.0.113.1):
-
Pull and run the Xray Docker container:
docker pull teddysun/xray:25.9.11 docker run -d \ --name xray_lb \ -p 4700:4700 \ --restart always \ -v /etc/xray:/etc/xray \ teddysun/xray:25.9.11 -
If you are using
firewall-cmdpackage, don't forgot to open the Shadowsocks port.firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=4700/tcp firewall-cmd --reload
Backend Servers Setup
Repeat these steps on both backend servers (e.g., IPs: 10.0.0.2 and 10.0.0.3).
These will accept traffic from the LB.
-
Run the Docker container.
docker pull teddysun/xray:25.9.11 docker run -d \ --name xray_backend \ -p 4800:4800 \ --restart always \ -v /etc/xray:/etc/xray \ teddysun/xray:25.9.11 -
Open the inbound port (e.g.,
4800/tcp) in the firewall, as above.
Step 5 - Client Configuration
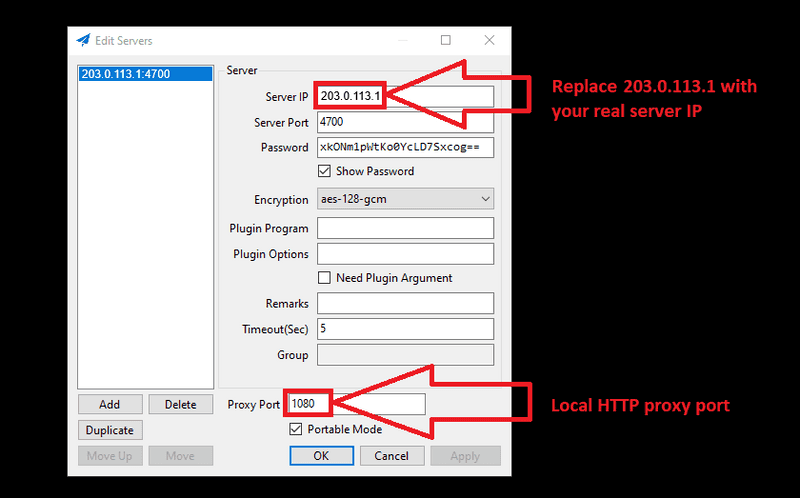
I will use curl to connect and test the connection via the Shadowsocks app on Windows.
This picture shows you how to set up the config and test your load balancer via the Shadowsocks local HTTP proxy.
curl --proxy http://127.0.0.1:1080 https://ip.hetzner.comConclusion
You have now set up a resilient Xray proxy with Shadowsocks and load balancing on Rocky Linux via Docker. This allows you to scale your setup across Hetzner servers.
If you encounter issues, check Xray documentation here.