Introduction
duf is a utility for a much better drive/filesystem overview as an alternative to df.
It is an open source project from Christian Muehlhaeuser written in Go programming language.
Prerequisites
- Any server you have at least root access for with a Linux based distribution
- If you are not working with the root user you may add the
sudocommand in front of all following console commands
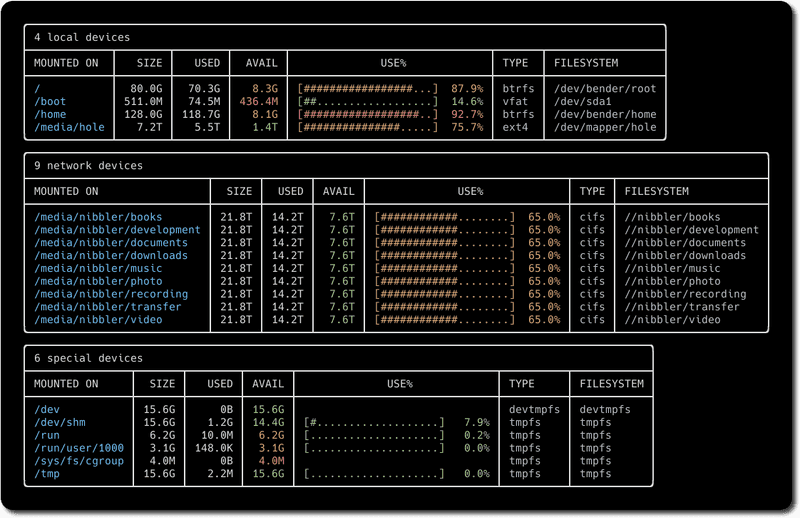
Screenshots
Screenshot from GitHub.com, License: MIT
Step 1 - Installation
The installation of duf can be done either via the already compiled packages or by installing it directly from the source code.
We recommend installing the already compiled packages.
Installation from Packages
For installing duf within the well-known operating systems there are availabe pre-compiled packages to download at the official GitHub repository: github.com/muesli/duf/releases
Hint: Please be aware of the fact, you need to download the correct package for your Linux Distibution and architecture from the link above. To download the packages you can take advantage of wget. Please see an example below:
$ wget https://github.com/muesli/duf/releases/download/v0.6.2/duf_0.6.2_linux_amd64.debUbuntu
You can install duf directly with the package manager or by using Snap.
Please see the hint above for downloading the package from GitHub first (keep in mind, you may need to adjust the filename). Once done, you can continue with this command to install the package using the package manager:
$ apt install ./duf_0.6.2_linux_amd64.debIf you want to use Snap instead, you can install duf using the following command:
$ snap install duf-utilityDebian
Installing duf under Debian can be done by taking advantage of apt.
Please see the hint above for downloading the package from GitHub first (keep in mind, you may need to adjust the filename). Once done, you can continue with this command to install the package using the package manager:
$ apt install ./duf_0.6.2_linux_amd64.debCentOS
For CentOS a pre-build package is available but unfortunately it is not included within the officical package reposiotries. duf can be installed by the local package installer yum.
Please see the hint above for downloading the package from GitHub first (keep in mind, you may need to adjust the filename). Once done, you can continue with this command to install the package using the package manager:
$ yum localinstall duf_0.6.2_linux_amd64.rpmOther Operating Systems
duf can also be installed on FreeBSD, macOS and Windows but this is out of scope of this guide. You can use the Installation from the source code instead, also you can find the official instructions at github.com/muesli/duf#installation.
Installation from Source Code
For installing duf from the source code you need a working Go environment (Go 1.12 or higher is required). You can find the official installation instructions from Go at golang.org/doc/install.
Afterwards, the program package can be compiled from the source code after the repository has been cloned with git. Only a few commands are needed for compiling:
$ git clone https://github.com/muesli/duf.git
$ cd duf
$ go buildStep 2 - Using duf
You can get started by just entering the main command without any arguments:
$ dufIf you want to see the information of specific devices or mount points you can also pass a path to duf:
$ duf /homeBy default, not all filesystems and devices are displayed by duf (for example BetterFS). To display all detected entries you can run the following command:
$ duf --allFiltering
It is also possible to hide and show some groupings if they are not relevant for you:
$ duf --only local,network,fuse,special,loops,binds
$ duf --hide local,network,fuse,special,loops,bindsOf course, this is also possible for the corresponding file systems:
$ duf --only-fs tmpfs,vfat
$ duf --hide-fs tmpfs,vfatDisplay Options
The columns of the tables can also be customized to sort by the size of the entries, for example:
$ duf --sort sizePossible option values are listed below:
- mountpoint
- size
- used
- avail
- usage
- inodes
- inodes_used
- inodes_avail
- inodes_usage
- type
- filesystem
Also, the displayed columns themselves can be specified. Possible options are the same as before:
$ duf --output mountpoint,size,usageJSON Output
In order to be able to further use the information collected by duf, the output can also take place in JSON format instead of in a table. For this you can use the following argument:
$ duf --jsonConclusion
duf is a great little program that makes it easier to view existing storage devices and file systems and understand their mappings.